OIE Mentor Supports Innovators’ Growth and Potential
Office of Innovation and Entrepreneurship 2025 James “Chip” Hanlon Volunteer Mentor of the Year:... Read more
If you are thinking about exploring the possibility of commercializing your technology via a startup then you are in good company. Many Pitt faculty have been down this route, and we have supported the creation of 60+ faculty-led startups over the last five years.
The journey varies for each inventor, and we have multiple entry points to the process from initial concept development through to securing funding. We run cohort-based programs as well as providing asynchronous learning opportunities. From refining your idea, understanding your customer needs, defining the value proposition of your innovation and more through to preparing for funding negotiations or accessing SBIR/STTR grants, we’re here to help.
Connect with our team startup@pitt.edu and we will work with you to identify a good path forward, providing you with expert help via our internal team, access to a mentor network and leveraging our programming in order to maximize the opportunity that you want to explore.
In the meantime, if you’re interested in learning more, you can access our online resource of curated videos and materials that provide a quick-look summary through to more in-depth discussion of a range of topics that you will find extremely useful as you consider the route of startup creation.
The Business Model Canvas has become the go-to tool for startup companies and established businesses when evaluating the potential of bringing a a new product or technology to market.
Business Model Canvas – An Introduction
A two-minute overview of the Business Model Canvas (BMC)
The BMC – 9 Steps Explained
Each of the 9 segments of the Business Model Canvas are explained including how they relate to one another (~10 minutes)
Alex Osterwalder Explains Business Model Canvas in Detail
Alex Osterwalder, creator of the Business Model Canvas, discusses in-depth (~42 minutes) and describes an example of how it helped well-known businesses grow.
Additional Resources
BMC Template
Download your own, editable Business Model Canvas to get started.
Business Model Explained with Examples
A 17-minute video that carefully explains each of the 9 segments of the BMC. The video leads the viewer through how a real business – Google – might fill out the BMC.
Business Model Canvas – Examples
This article includes examples of the BMC for the auto industry and Amazon. Also includes a downloadable template.
Business Plans
Here the Pitt library introduces you to the various ways to write a business plan and provides you with suggested resources to complete them.
When it comes time to seek investors or partners for your startup, you will need a compelling pitch deck to present your big idea clearly and concisely.
The Best Pitch Decks – Common Threads
A short video chat with Sequoia Capital (investors in Zoom, DoorDash, 23 and Me, etc.) about what elements must be in your pitch to attract investor interest.
Why Investors Say NO
5 points of very practical advice for your pitch, regardless of industry (~10 minutes)
How to do a Great Pitchdeck with Guy Kawasaki
This “no holds barred” presentation provides advice on how to make a successful pitch from renowned startup expert Guy Kawasaki. (~20 minutes)
Additional Resources
Pitch Template
What should your pitch deck consist of and what are the essentials you should discuss? Download our Pitt-branded template to create your own pitch deck.
Bonus Section – Storytelling
Now that you know what makes up a strong pitch, telling a story as you present the key elements of a pitch (Problem, solution, business model etc.) will help engage your audience and retain the messages you want to send in your pitch. Below find two videos that address the importance of storytelling and how to weave a story into your pitch.
How To Tell a Compelling Story
In just eight minutes, Dream-it-Dose explains how to use a story to communicate the key aspects (problem, value proposition etc) of your business. By use of a Fairy Tale analogy, this easy to understand and fun to watch video will help investors retain the information you communicate. to them.
The Art of Persuasive Storytelling
Invest 12 minutes of your time taking a look at this TED talk and learn why storytelling is important. The presenter, Kelly Parker, explains how a story starts with understanding your audience (customer), features a problem and the pursuit of its solution and concludes with how to make a successful ask.
Just for Fun!
Take a look at this 36 minute video by the lead story teller behind many of Pixars animated films (Toy Story, Up, Insideout”. This is both entertaining and useful. Find 2-3 tidbits to use in your business pitch!
By using the Value Proposition Canvas (VPC) learn how to describe the value a product or service promises to deliver to a customer. Investors will expect an entrepreneur to concisely explain the value proposition before investing.
Value Proposition Explained
Learn the basic outline of the Value Proposition Canvas. (~2 minutes)
Value Proposition Explained and Example
The elements of the value proposition canvas are further explained by use of the VPC for Uber as an example.
Alex Osterwalder – Value Proposition Design
Hear the complete story and description of the Value Proposition Canvas by its creator, Alex Osterwalder. His entertaining lecture includes short, optional, exercises for you to consider using. (~ 1 hour)
Additional Resources
Value Proposition Template
A free downloadable template where you can describe your gain creators, pain relievers, and products/services.
How do you ensure that your product or service will solve a customer’s problem effectively and cost efficiently? You talk to potential customers to find out.
Customer Discovery – Best Practices
This very complete slide deck will lead you through the customer discovery process – why’s and how’s. Includes tips and tricks.
Customer Discovery – Search for The Holy Grail
An explanation of what customer discovery is and why it is important. (~ 3 minutes)
Customer Discovery – Testing Product Hypothesis
Steve Blank, father of the “lean startup” concept, discusses the role a company founder plays in customer discovery and why getting out and talking to customers is critical.
Customer Discovery and Development
This presentation uses examples to explain customer discovery, the risk of introducing biases and introduces the concept of the customer’s journey
Additional Resources
Talking to Humans
Free download of this must-read book (~60 minute read) about how to conduct customer discovery and why it is important. It is offered free to students, faculty, etc. after a quick form submission.
Gain an understanding of how to determine the size of the market your product and/or service addresses and what segment(s) of that market you can effectively reach initially, while expanding your focus to other segments over time.
Total Available Market: How to Build a Startup
This short video explains Total Addressable Market (TAM)
Market Sizing – TAM, Mistakes to Avoid
A very practical explanation of how to, and how NOT to calculate market size.
How to Calculate Market Size – TAM, Bottom Up
Learn how to conduct a bottom-up estimate of the Total Addressable Market (TAM) for your product. Includes examples. (~15 minutes)
Learn how to analyze existing offerings in the marketplace and explore how to use this information to differentiate your offerings.
Competitive Analysis and How to Present it
A venture capitalist discusses three ways to present your competitive analysis to an audience.
How to Conduct Competitive Analysis
Easy to follow video covering how to conduct a competitive analysis (~ 10 minutes)
Competitive Analysis: 14 Steps
More detail on performing a competitive analysis
Additional Resources
How to Conduct and Prepare a Competitive Analysis
This helpful article includes a complete “how to” with key questions to address, a list of sources to find information on your competitors (note: the Pitt library has access to most of the sources listed), and several other useful suggestions and formats to help assemble competitive information.
Understanding company formation is crucial for startups because it lays the foundation for the legal and financial structure of the business. Choosing the right entity type, such as a limited liability company (LLC) or a corporation, can have significant implications for factors such as taxation, liability, and funding opportunities. Additionally, properly registering the company with the appropriate government agencies and adhering to local laws and regulations is essential to avoid legal complications in the future. By understanding the process of company formation, startups can ensure that they establish a solid foundation for their business and set themselves up for long-term success.
A capitalization table is a snapshot of the ownership structure of a company, outlining the different types of securities and the percentage of ownership held by each shareholder at a specific moment in time. This document is useful for tracking ownership changes and understanding the dilution of equity over time.
Cap Table Fundamentals– Art of Startup Finance
Check out this exceptional 4-minute video that explains the fundamentals of a capitalization table, which is a comprehensive record of who holds equity in your company. The video also sheds light on why investors are keen to know the identities of the stakeholders.
What is a Cap Table?
This 18-minute video provides a detailed yet accessible explanation of the components of a capitalization table. It covers the four different states of stock and clarifies the distinction between common and preferred stock.
Don’t Let This Happen To Your Startup! — Cap Table Tutorial
What is a Term Sheet?
In less than five minutes, you can grasp the fundamentals of a “term sheet,” which outlines the key terms and conditions for a potential investment in a clear and concise summary.
The Biggest Term Sheet Mistakes Founders Make
From the viewpoint of a venture capitalist, this 18-minute, quickly paced video provides very direct and practical information on mistakes Founders often make when negotiating a term sheet with an investor.
Startupedia’s Term Sheet Panel
In an hour, a panel of lawyers review a term sheet section by section. Watching this video can help you be more efficient in your discussions with your own attorney.
As a startup considering incorporation, it’s important to understand the difference between a Limited Liability Company (LLC) and a C-Corporation (C-Corp) and their respective advantages and disadvantages. The following articles present some basic information on the selection of a form of corporation for your startup.
Choice of Business Entity: Pros & Cons of Corporations and LLCs
This article discusses the pros and cons of three of the most common business entity types: C-Corporations, S-Corporations and Limited Liability Companies (LLCs). C-Corporations are generally attractive to venture capital funds and tax-exempt investors, but they have potential double taxation. S-Corporations are taxed in a manner similar to a partnership, which means that income and losses pass through to the stockholders, but they are subject to strict requirements that must be met. LLCs are flexible in their corporate governance and taxation structure, but may not be as attractive to large investors as C-Corporations.
This article provides an opportunity to examine the key resemblances and disparities between a limited liability company (LLC) and a corporation (Inc.), encompassing their impact on management structure, approach to profit and loss distribution, and method of tax payment to the IRS.
Building a Startup Team
The first of a series on start-up teams, this six-minute video begins with the basics of why a team is important, especially when starting up a company.
How Do You Convince Someone to Join Your Team?
How to Find the Right Co-founder
Company value refers to the perceived worth of a business, as determined by various factors such as its revenue, market position, intellectual property, and other assets.
How To Value a Seed Stage Company
How to Value Your Startup
How Startup Valuations Work
A comprehensive video demonstration of how various parties in a transaction perceive and calculate valuations.
Find Helpful Legal Documents
On Cooley you can fill out your own DE Corporation, Series Seed document generator which simplifies the process of legal documents for startups.
Learn about Equity Series
An Equity 101 course on everything you need to understand equity in private companies.
Produced by the Kauffman Foundation, presented in nine segments the following 22, short videos (just over 62 minutes in total) provide the budding entrepreneur with a solid overview of the five layers of the “Finance Pyramid”. In easy-to-understand terms viewing the entire collection of video material teaches the non-financially trained person about financial statements, forecasting/budgeting and monitoring financial performance as an indicator of business growth.
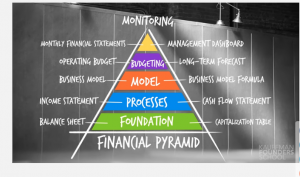
Extra Content:
Planning is Critical for Success
In this introduction the “Finance Pyramid” explains how finance underpins your businesses goals and strategies. (3-minute video)
A short case presentation on why financial information is critical to making plans for your business. (2-min video)
I Had to Rebuild Our Books
An example of why having company financial record keeping and producing financial statements is important to do right, right from the start of your venture. (2-min video)
Balance Sheet
The foundation of your financial structure is your balance sheet. It provides the details of your assets and your liabilities, and it also shows your shareholders equity. In this session, you will learn the basic elements of the balance sheet, and how investors will assess the health of your company by analyzing your balance sheet.
Extra Content:
Discipline is Critical
Why understanding your balance sheet and capitalization table is important. Stresses the need for expertise and discipline in constructing your financial statements. (1-min video)
Capitalization Table
The details of the Shareholders Equity section of your Balance Sheet are shown in your Capitalization Table, which is maintained as a separate report. The “Cap Table” shows how much of the company each shareholder owns, and in what form — common stock, preferred stock, options, or warrants. Investors will want to look at your cap table to understand how you have distributed your common stock and how you have raised investment capital. (4-min video)
Income Statement
Your income statement shows the performance of your company over a period of time and reveals important information about how efficiently you are running your business. Understanding your income statement, and what it tells you about the health of your business, is critical. (6-min video)
Extra Content:
More Than a Bookkeeper
A startup CEO explains the reasons why you need experienced financial professionals involved in your company. (1-min video)
Cash Flow
Your cash flow statement shows where your cash is coming from, and where it is going. Sometimes known as “sources and uses of funds,” this financial report is an important complement to your income statement and balance sheet. Investors want to see that you know the difference between your net income and your net cash flow.
Extra Content:
Avoiding the Red Zone
How understanding cash flow can keep you out of operating your company in the “red zone” – always needing more cash and not knowing where it will come from. (2-min video)
Losing Credibility
Not understanding how to use your financials to control your business causes problems that negatively impact your credibility with investors and customers. (1-min video)
Invoicing at a Positive Rate
Tips on how and when to invoice your customer. (2-min video)
Your Business Model Formula
The engine of your business is your business model. In your business model you develop your strategies and tactics for making money as a business. Learn how to convert those strategies and tactics into financials. (5-min video)
Extra Content:
Historical Data Impacts Current Numbers
Examples of how historical operating costs can be used to help create a five year financial plan. (2-min video)
Budgets Force You to Focus
Budgets help you focus your business operations, especially when operating on a shoe string. (2-min video)
Your Operating Budget
Developing a useful operating budget is extremely valuable, and extremely challenging. Learn the keys to building an operating budget and using it to track what is going well, and head off the things that aren’t. Suggests creating your own forecast by first understanding the key cost and revenue drivers for your business. (6-min video)
Long-term Financial Projections
Forecasting is usually the toughest part of startup finance for entrepreneurs. But learning how to forecast and budget are critical. The point is not to try to predict the future. The point is to build a financial model that you can improve over time and that shows an investor that you have carefully thought through your business model. (5-min video)
EExtra Content:
Minimize Your Overhead
Solid advice for the importance of keeping overhead low in order to increase the chance for success. (2-min video)
Understanding Numbers Over Accuracy
Financial projections are more important to demonstrate your knowledge of your business to an investor, than to be extremely accurate. (1-min video)
Your Performance Metrics
Get in the habit of producing good financial reports every single month. But you need more than just standard financial reports. You need a Management Dashboard that monitors critical metrics that may not pop out of your accounting reports. (4-min video)
Extra Content:
Planning is Critical for Success
Planning for growth and understanding the cost of growth helps businesses succeed and avoid surprises. (2-min video)
Keeping track of the right financial metrics makes you a good steward of capital. (2-min video)
Diversity is essential in startups as it drives innovation by bringing together varied perspectives and experiences. Diverse teams generate creative solutions, understand diverse markets, and make better decisions, leading to a competitive edge. Embracing diversity also attracts top talent, enhances adaptability, and aligns with ethical principles, contributing to the startup’s long-term success and positive brand perception.
How Diverse Teams Drive Innovation
TED talk veteran and expert in how diversity drives innovation, Rocio Lorenzo, presents data from a study she conducted on how important diversity is to an organizations efforts to innovate. Link includes access to a transcript and data. (4-min video)
Diversity and Inclusion As A Source of Innovation in Organizations
General Navigation Guidelines for FDA
This written document contains dozens of links to government sources that are quite helpful to the medical product developer/innovator. The information is written for an entrepreneur to easily understand.
How to get your Medical Device Through the FDA – Michael Nilo
This presentation, originally part of the SHRS Innovation Seminar Series, leads you through the steps leading to FDA approval/clearance of a medical device. (1-hour long)
Most startups need a place to meet with clients and have meetings but the starting costs of a startup make renting out an entire office space an option that is costly and not a priority. Enter co-working space or accelerators that provide space for your startup.
Co-working spaces are shared workspaces with added perks like wi-fi, private offices, printing/photocopying, access to event space, coffee, networking opportunities, and more. Check out the ones in Pittsburgh listed below.
Startup accelerators remain one of tech’s most popular ways to get a business up and running and there are plenty to select from for new startups.
With hundreds of programs to choose from — the most popular receive more than 5,000 applications for each class — and the average program taking 6% of equity in any hosted company, not all accelerators are created equal. Check out our lists below for local accelerators in the Pittsburgh area.
AlphaLab provides early-stage technology companies with an extensive mentor network, educational sessions with industry leaders, and a rich entrepreneurial work environment within a nationally ranked accelerator program.
AlphaLab Gear is consistently ranked as a top-20 accelerator nationwide. They provide early-stage physical product companies with an extensive mentor network, educational sessions with industry leaders, and a rich entrepreneurial work environment.

AlphaLab Health is a healthcare and life sciences accelerator, which supports early-stage tech startups in their efforts to bring innovations to market, navigating key risk points of scientific, clinical, and commercial development. AlphaLab Health is a program of Innovation Works in collaboration with Allegheny Health Network.
![]()
Ascender is a Pittsburgh-based non-profit organization providing mentorship, programming, strategic partnerships, funding and collaborative workspace to early-stage startups across all industries and growth models.

The Blast Furnace is the Pitt student accelerator providing access to a deep mentor network, inspirational co-working space, and a rich curriculum preparing students for creating and growing their business ideas.
 LifeX Labs is a life science startup accelerator focused on providing early-stage companies with the support, resources and ecosystem they need to be successful.
LifeX Labs is a life science startup accelerator focused on providing early-stage companies with the support, resources and ecosystem they need to be successful.
Idea Foundry is an accelerator program intended to help speed up the process of commercialization.
Learn More: 30 Best Startup Accelerators
Dream IT Dose Library
A collection of 5-minute videos produced by DreamIt Ventures provides practical advice from the vantage point of the real-world operations of a venture capital firm.
Kaufmann Learning Paths
Video segments (with transcripts) on a wide range of topics of interest to entrepreneurs. Presented in bite size segments, this collection is well produced, easy to understand
Federal Funding Dates
Federal agency funding dates including SBIR, STTR, and more.
University members are encouraged to engage in outside activities, including launching startup companies based on Pitt IP, consistent with Pitt’s mission to transfer knowledge in science, technology and healthcare and which benefit society. Pitt members are also permitted to have management or officer positions in outside entities and receive financial benefit from such activities, so long as these interests do not interfere with their University duties or distort the judgments expected of them.
Pitt Licensed Start-up Companies (LSCs) are non-publicly traded companies that:
Relationships with these companies and their interactions with the University are governed by University Policy RI01.
All relationships with these companies, whether paid or unpaid, require the approval of the Conflict of Interest Committee (COIC) following the LSC COI approval process and must follow all Outside Activity requirements.
Contact our New Ventures team at startup@pitt.edu for guidance and support on the University’s Conflict of Interest process for Pitt LSCs.
Licensing your startup’s technology or intellectual property is a crucial step in maximizing its potential. Conduct thorough market research, identify potential licensees, and craft a compelling value proposition to secure favorable agreements.
Each year, the Office of Innovation and Entrepreneurship at the University of Pittsburgh executes over one hundred option and license agreements with companies eager to commercialize Pitt’s groundbreaking discoveries.
Due to the extensive research conducted at the University, the innovations available for licensing span a wide range of fields, including life sciences, physical sciences, education, computer sciences, and more.
Licensing terms for these innovations can vary based on several factors, typically including patent expenses, royalties on sales, upfront license fees, annual maintenance fees, equity in new startups, and development milestones. While we start with standard terms, we are open to negotiation within the framework of the agreement to ensure a mutually beneficial outcome for both our partners and the University.
Our standard agreement templates are provided. These sample agreements are meant to provide an example of the agreements and terms that are common when working with the University of Pittsburgh and are subject to change.
A Confidential Disclosure Agreement (CDA) is essential when sharing proprietary information about university technology with external parties. This includes any information not yet publicly available through patents or publications. Having a CDA in place before disclosing confidential information is crucial to protect our ability to pursue patent protection.
Purpose and Process: Confidential Disclosure Agreements for evaluating or discussing licensing or related business partnerships are managed by the Innovation Institute. All forms must be signed by the appropriate university representative, typically the Director of the Innovation Institute, to be legally binding. Documents not processed through the proper channels may jeopardize intellectual property rights. If you are unsure who the proper representative is, please contact the Innovation Institute.
All provisions in the document templates below are subject to change. Additions, eliminations, or revisions may occur. Please note that all communications and discussions are tentative until a written agreement is executed by both parties.
Forming a New Company?
Have an Existing Company?